Microporous Insulation Board, Heat Insulation materials for Ladle
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Micropore Insulation Board ,Heat Insulation materials
| Type: | Other Heat Insulation Materials | Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | |
| Model Number: | M5100 | service temperature, max.: | 1150 C | Thermal conductivity, @800 C: | 0.035 W/m.K |
| typical density: | 280 kgs/m3 |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | wooden cases |
| Delivery Detail: | 10 days |
Product Description
M5100 Panel is rigid finishing from microporous technology , with opcified blend of filament reinforced fumed silica, which provides a superb thermal performance.
It is an ideal back-up insulation for various industry where the high temperature is needed, with a long time exposure of 1150 °C at highest.
M5100 Panel ---Various coverings : Naked Panels, Aluminium Foil covering, E-class Fibre Cloth Covering, Fibre Paper covering.
M5100 Panel—Four Grades available : 850 , 1000, 1100, 1200
Properties & Advantages
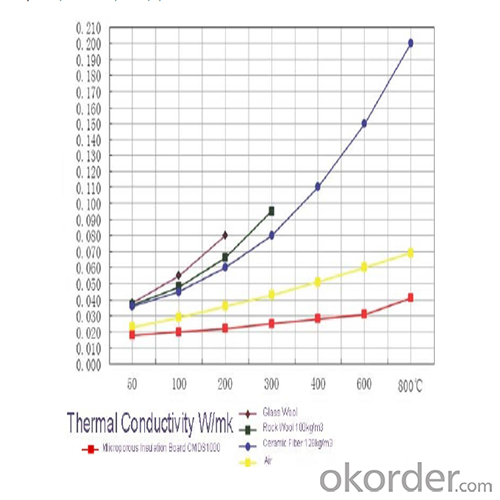
Extremely low thermal conductivity
High thermal stability
High compressive strength
No harmful respirable fibres
Free of organic binders
Environmentally friendly
Resistant to most chemicals
Non combustible
Easy to handle
Typical Applications
Back-up insulation in industrial furnaces
Fuel cells (SOFC)
Thermal Batteries
Aluminium industry ( launders,Smelter.etc. )
Glass & ceramics industry
Petrochemical industry (cracking furnace, reformer)
Black box & VDR (Voyage Data Recorder)
Data loggers
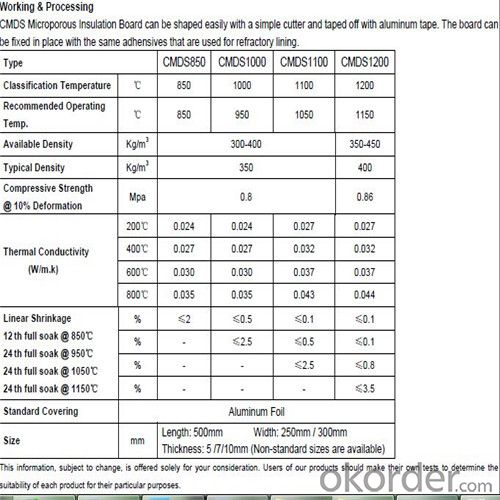
Working & Processing
M5100 can be shaped both manually and with stationary wood processing machinery. They can be cut, sawn, drilled and punched. The boards can be fixed in place with glue or by mechanical means such as anchors, pins and clips.
Technical Data for for Micropore Insulation Board ,Heat Insulation materials
| Description | MISSION STD Panel M5100 | ||||
| Classification Temperature | 0C | 850 | 1000 | 1100/1100S | 1200/1200S |
| Long time Exposure | 850 | 950 | 1050/1000 | 1150/1100 | |
| Nominal Density | [kg/m3] | 260-280 | 260-280 | 400-450 | 450-550 |
| Typical Density | 280 | 280 | 450 | 500 | |
| Compression Strength | [MPa] | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.8 |
| @10% deformation (ASTM C-165) | |||||
| Thermal Conductivity | |||||
| 200 0C | W/m.K | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.024 0.028 | 0.027 0.029 |
| 400 0C | W/m.K | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.028 0.032 | 0.032 0.035 |
| 600 0C | W/m.K | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.032 0.038 | 0.037 0.042 |
| 800 0C | W/m.K | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.035 0.045 | 0.043 0.046 |
| Specific Heat Capacity | |||||
| 200 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| 400 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| 600 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| 800 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 1.08 |
| Linear Shrinkage | |||||
| 12h full soak @ 850 0C | % | ≤2 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.1 ≤0.1 | ≤0.1 ≤0.1 |
| 24h full soak @ 950 0C | - - - | ≤2.5 | ≤0.5 ≤0.1 | ≤0.5 ≤0.5 | |
| 24h full soak @ 1050 0C | - - - | - - - | ≤2.5 - - - | ≤2.5 ≤2.5 | |
| 24h full soak @ 1150 0C | - - - | - - - | - - - - - - | ≤3.5 - - - | |

Standard Dimension:
1000(900)×600(500)×5-20mm
We can also manufacture the special dimensions as customers need.
Q1:Are you a manufacture or trader?
A:Factory+trade(mainly factories,at the same time,we operates other related products).
Q2:Can we visit your factory?
A:Sure,welcome at any time,seeing is believing.
Q3:What's the MOQ of trial order?
A:No limit,We can offer the best suggestions and solutions according to your condition.
Q4:Which payment terms can you accept?
A:T/T,L/C,Western Union,Moneygram,Paypal are available for us.
Q5:After an order is confirmed,when to deliver?
A:15-25days after deposit.
Q6:Is your company accept customization?
A:We have own factory and excellent technical team,and we accept OEM service.
Q7:How about your company's certification?
A:ISO9001 and Test Report,also we could apply other necessary certification.
Q8:How to slove the quality problems?
A:If the products are not confirmed to customer samples or have quality problems,our compay will be responsible to make compensation for it.
Q9:Can you offers samples?
A:Of coures,samples are free but freight paid by the buyers.
Q10:What is the service life of your bricks?
A:The service life of different bricks is unlike.It also depends on your using condition and method.
Thanks for your coming in,if there is any question,I will be glad to help you.
- Q:Are glass fiber textiles resistant to moisture absorption or retention?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles are highly resistant to moisture absorption and retention.
- Q:What are the different surface treatments available for glass fiber textile?
- There are several different surface treatments available for glass fiber textiles, each offering unique properties and benefits. Some of the most common surface treatments include: 1. Sizing: Sizing is the most basic surface treatment for glass fiber textiles. It involves applying a protective coating to the fiber strands to improve their handling and processing characteristics. Sizing agents can also provide some resistance to moisture and abrasion. 2. Silane treatment: Silane treatment involves applying a thin layer of silane coupling agents to the glass fiber surface. These agents create a chemical bond between the glass fibers and resin matrices, improving the adhesion between the two materials. Silane treatment enhances the mechanical properties, moisture resistance, and durability of glass fiber textiles. 3. Coating: Coating is a surface treatment that involves adding a thin layer of a specific material onto the glass fiber surface. The coating can be made of various substances such as polymers, metals, or ceramics. Coatings can provide additional protection against abrasion, chemical attack, UV radiation, or heat. 4. Laminating: Laminating is a surface treatment where a layer of another material, such as a film or fabric, is bonded to the glass fiber textile. This treatment can enhance the overall strength, flexibility, and surface characteristics of the textile. 5. Flame retardant treatment: Flame retardant treatment is used to improve the fire resistance of glass fiber textiles. It involves applying special chemicals or coatings that can prevent or slow down the spread of flames when exposed to heat or fire. 6. Anti-static treatment: Anti-static treatment is applied to prevent the buildup of static electricity on the surface of glass fiber textiles. It involves adding conductive materials or coatings that allow the dissipation of electrical charges, reducing the risk of static discharge. These different surface treatments allow glass fiber textiles to be customized for specific applications, improving their performance, durability, and functionality in various industries such as automotive, construction, aerospace, and electronics.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be ironed?
- Glass fiber textiles cannot be ironed; doing so may result in melting, burning, or deformation. It is crucial to adhere to the manufacturer's care instructions, as they typically advise against exposing these textiles to high heat sources like irons.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be used for making sports equipment?
- Glass fiber textiles, also known as fiberglass, possess characteristics that make them well-suited for creating sports equipment. With their lightweight nature, durability, and impressive strength-to-weight ratio, they can be utilized for various sporting purposes. Equipment such as tennis rackets, golf clubs, hockey sticks, and protective gear like helmets and shin guards can all be manufactured using glass fiber textiles. These textiles exhibit flexibility and resilience, contributing to enhanced sports performance, providing better control, power, and accuracy. Furthermore, fiberglass materials offer resistance against moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation, making them an excellent choice for outdoor sports equipment that endures harsh environmental conditions. Ultimately, glass fiber textiles have a proven track record as a dependable and high-performing material in the production of sports equipment.
- Q:How are glass fiber textiles used in the electronics industry?
- The electronics industry extensively utilizes glass fiber textiles for various purposes. Insulation is one of the main applications of these textiles. Due to their exceptional resistance to heat and excellent electrical insulation properties, they are ideal for creating protective barriers around sensitive electronic components. This insulation helps prevent heat transfer and electrical short circuits, ensuring the safe operation of electronic devices. Another use of glass fiber textiles is in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). PCBs act as the backbone of electronic devices, facilitating the necessary connections between different components. Glass fiber textiles, specifically epoxy glass laminates, serve as the base material for PCBs. These textiles are impregnated with epoxy resin and layered with copper sheets, resulting in a strong and durable substrate for the circuitry. Furthermore, glass fiber textiles are employed to reinforce electronic components. By incorporating glass fibers into the manufacturing process of connectors, switches, and housings, the overall strength and structural integrity of these components are enhanced. This reinforcement allows for better resistance against mechanical stress, such as impacts or vibrations, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices. Additionally, glass fiber textiles have applications in electromagnetic shielding. They can be woven into conductive fabrics, which are used to create shielding enclosures or covers for electronic devices. This shielding prevents electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) from affecting the performance of sensitive electronic circuits. By effectively blocking these interferences, glass fiber textiles contribute to maintaining the quality of signal transmission and reception in electronic devices. Overall, glass fiber textiles play a crucial role in the electronics industry by providing insulation, serving as PCB substrates, reinforcing electronic components, and contributing to electromagnetic shielding. Their thermal and electrical insulation properties, combined with their strength and durability, make them an essential material for ensuring the proper functioning and protection of electronic devices.
- Q:What are the weight and thickness options for glass fiber textiles?
- Glass fiber textiles come in various weight and thickness options to meet specific needs and applications. Weights are typically measured in oz/yd² or gsm, ranging from lightweight fabrics at 3 oz/yd² or 100 gsm to heavy-duty textiles exceeding 30 oz/yd² or 1000 gsm. In the same way, thickness can vary depending on desired strength and functionality, measured in mils or µm. Glass fiber textiles can be as thin as 10 mils or 0.25 mm, while thicker options can surpass 100 mils or 2.5 mm. The weight and thickness of glass fiber textiles are tailored to the intended use and requirements of the application. Manufacturers and suppliers offer a wide range of choices to accommodate industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and marine, among others.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be used in military applications?
- Glass fiber textiles are indeed applicable in military contexts. Renowned for their robustness and durability, these textiles are well-suited for diverse military purposes. They find utility in fabricating military uniforms, bulletproof vests, and other protective equipment. Their ability to withstand high temperatures, flames, and chemicals is vital in military settings. Moreover, glass fiber textiles are employed in constructing military tents, camouflage nets, and other textile structures. In summary, glass fiber textiles offer a multitude of advantages and can be effectively employed in a range of military applications.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be used in acoustic insulation?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in acoustic insulation. Glass fiber textiles are known for their excellent sound absorption properties due to their porous structure and ability to trap sound waves. They are commonly used in applications such as acoustic panels, soundproof curtains, and insulation materials to reduce noise levels and enhance acoustic comfort.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be used in the production of furniture?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in the production of furniture. Glass fiber textiles, also known as fiberglass textiles, are made from fine strands of glass fibers that are woven together to form a fabric. This fabric is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and pests. In furniture production, glass fiber textiles can be used in various ways. They can be used as reinforcement materials to provide additional strength and stability to furniture structures. For example, glass fiber textiles can be used to reinforce the frames of chairs, sofas, or tables, making them more resistant to bending or breaking. Glass fiber textiles can also be used as upholstery materials. They can be woven or knitted together to create a fabric that is then used to cover furniture surfaces. This can provide a unique and modern look to furniture pieces, as well as enhance their durability and resistance to wear and tear. Furthermore, glass fiber textiles can be molded into different shapes and forms. This allows furniture designers to create innovative and lightweight furniture designs that are not possible with traditional materials. Glass fiber textiles can be molded into intricate patterns, curves, or even 3D structures, offering endless possibilities for furniture design. Overall, glass fiber textiles offer numerous advantages in furniture production, including strength, durability, resistance to heat and chemicals, and design flexibility. Therefore, they can be a suitable choice for manufacturers looking to create high-quality and innovative furniture pieces.
- Q:Are glass fiber textiles resistant to oil or grease?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles are resistant to oil and grease. Glass fibers have a non-reactive nature, which makes them highly resistant to most chemicals, including oil and grease. This resistance is due to the fact that glass fibers are made from inorganic materials and do not contain any organic compounds that can be easily degraded by oil or grease. Therefore, glass fiber textiles are commonly used in applications where resistance to oil and grease is required, such as in the automotive industry, industrial equipment, and oil and gas pipelines.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Microporous Insulation Board, Heat Insulation materials for Ladle
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Related keywords