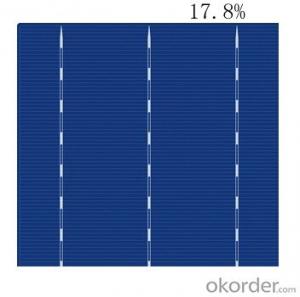
Monocrystalline Vs Polycrystalline Wikipedia
Monocrystalline Vs Polycrystalline Wikipedia Related Searches
Solar Panel Inverter For Rv Solar Panel Kit With Inverter Inverter Used In Solar Panel Best Inverter Solar Panel Solar Panel On Roof Rack Solar Panel To 240v Inverter Solar Panel To Inverter Ratio Solar Panel Mini Inverter Solar Panel Inverter Battery Solar Panel Inverter BoxHot Searches
Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors Price Lorentz Solar Pumps Price Cost Of Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors Solar Panel Inverter Suppliers Tesla Solar Panel Inverter Solar Items Wholesale Type Of Inverter For Solar Price Of Silicon Solar Cells Best Type Of Solar Cells Solar Grade Silicon Price Type Of Solar Inverter Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors Price Lorentz Solar Pumps Price Cost Of Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors Solar Panel Inverter Size Solar Panel Inverter Suppliers Solar Inverter Solar Panel Tesla Solar Panel Inverter Solar Inverter Type 300Mm Silicon Wafer PriceMonocrystalline Vs Polycrystalline Wikipedia Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional Monocrystalline Vs Polycrystalline Wikipedia supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest Monocrystalline Vs Polycrystalline Wikipedia firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- Solar cells may not perform optimally in areas with high levels of volcanic ash. The ash particles can accumulate on the surface of the solar cells, blocking sunlight and reducing their efficiency. Regular cleaning and maintenance may be required to ensure the cells continue producing electricity effectively.
- Yes, solar cells can be used in greenhouses to generate electricity and power various systems within the greenhouse, such as lighting, ventilation, and irrigation. This helps reduce the reliance on traditional energy sources and promotes sustainable and eco-friendly practices in greenhouse farming.
- Temperature fluctuations can have a significant impact on solar cell efficiency. Generally, as temperatures rise, the efficiency of solar cells decreases. This is because higher temperatures can increase the resistance of the materials used in the solar cell, resulting in a decrease in the conversion of sunlight into electricity. Additionally, excessive heat can cause thermal stress and degradation of the solar cell's components, further reducing its efficiency over time. Therefore, temperature regulation and cooling mechanisms are crucial in maintaining optimal solar cell performance and maximizing energy production.
- The impact of snowmelt on solar cell efficiency is generally positive. When snow covers solar panels, it reduces their ability to generate electricity due to the lack of sunlight reaching the cells. However, as the snow melts and slides off the panels, it allows for maximum exposure to sunlight, thus improving the efficiency and energy production of the solar cells.
- Solar cells generally perform well in areas with high humidity and saltwater exposure. However, prolonged exposure to high humidity and saltwater can potentially degrade the performance and lifespan of solar cells. The humidity can cause moisture to accumulate on the surface of the solar panels, leading to reduced efficiency. Additionally, saltwater exposure can corrode the metal components of the solar cells, further impacting their performance. To mitigate these issues, manufacturers often use corrosion-resistant materials and coatings for solar panels deployed in coastal regions or areas with high humidity. Regular maintenance and cleaning can also help ensure optimal performance in such environments.
- Solar cells can still perform well in humid climates, although their efficiency might be slightly reduced compared to dry climates. The moisture in the air can cause some scattering of sunlight and create a film of water on the surface of the solar panels, which can decrease their efficiency. However, advancements in solar cell technology have been made to mitigate the effects of humidity, such as using anti-reflective coatings and self-cleaning mechanisms. Overall, solar cells can still generate electricity effectively in humid climates.
- Yes, solar cells can still generate electricity in cloudy weather, although their efficiency is reduced compared to when they are exposed to direct sunlight.
- Yes, solar cells can be used in agricultural farms. They can be installed on rooftops or open fields to generate clean and renewable energy. This energy can be utilized to power various agricultural operations such as irrigation systems, lighting, and machinery. Additionally, solar cells can help farms become more self-sufficient and reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources, thereby contributing to sustainable farming practices.